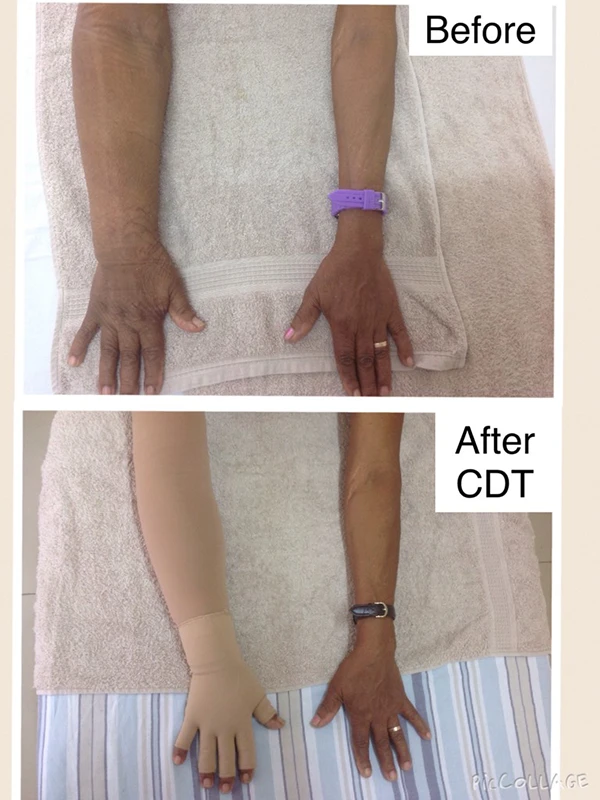
Lymphedema
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) is a comprehensive treatment for chronic extremity lymphedema. It combines four main components:
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
- Bandaging of the affected areas
- Remedial exercises
- Skin and nail care
CDT is delivered in two phases:
- Intensive Phase – Active treatment conducted by a certified lymphedema therapist.
- Maintenance Phase – Continued by the patient at home to maintain results.
When carried out with consistency and expertise, CDT delivers excellent results with no side effects, even in advanced cases. While the therapy is time-consuming and requires strong patient commitment, its effectiveness makes it the gold standard in lymphedema management.
More patients are now benefiting from CDT and successfully maintaining long-term limb reduction through dedicated home routines.
CDT in Mauritius
CDT is a new therapy in Mauritius, currently available only through Island Medical (Mauritius) Ltd in Tamarin.
Patients from vulnerable groups may qualify for a free initial consultation by contacting Link to Life and booking an appointment at our Vacoas or Pamplemousses branches.
CDT Therapist Qualifications
For a lymphedema therapist to be fully qualified in CDT, their training must include all four of the following:
- Basic and advanced MLD
- Lymphedema bandaging
- Remedial exercises
- Skin and nail care
- Basic and advanced MLD
- Lymphedema bandaging
- Remedial exercises
- Skin and nail care
Additionally, they must possess an in-depth understanding of:
- The anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of the lymphatic system
- Treatment approaches for primary and secondary lymphedema
- Indications and contraindications of CDT
- Correct techniques for measuring and fitting support garments

Safety and Monitoring
Although most lymphedema diagnoses can be made without invasive testing, an electrocardiogram (ECG) may be recommended before and during treatment to ensure patient safety.
Given the potential risks associated with lymphedema, ongoing supervision by a qualified physician is essential to ensure both safety and effectiveness throughout the therapy process.
Medications and Lymphedema
Diuretics, though commonly prescribed, usually worsen lymphedema. They remove water from swollen tissues but leave behind proteins, which attract water back once the effect wears off. This can lead to more swelling and, over time, cause the tissue to become fibrotic and hardened.
While new research is exploring surgical options and medication-based treatments, CDT remains the most effective and reliable method for managing lymphedema today.