Colon cancer screening
colon cancer: What You Need to Know
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer is a type cancer that develops from the cells that line the inner wall of the colon. Despite extensive research, the exact cause of colorectal cancer remains unknown. In most cases, the cancer starts as a small benign growth (a small non-cancerous tumor) that slowly develops and eventually becomes cancerous.

Facts
- Colon cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide
- It affects both men and women
- In 2021-2023, a total of 977 newcases of colorectal cancer were registered
- In 2021-2023, it's estimated that 318 males and 278 females died from colorectal This cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally.
Stages
- Stage 0 - abnormal cells are found only in the inner lining pf the colon
- Stage 1 - cancer has grown into the colon wall but hasn’t spread
- Stage 2 - cancer has spread through the wall of the colon but not to the lymph nodes
- Stage 3- cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- Stage 4 - cancer has spread to distant organs (like the liver or lungs)
Risk factors
You have a higher risk of colon cancer if you are:
- Age 60 and older
- Consume meals rich in red meat
- A cancer in other parts of your body
- Benign polyps
- An inflammatory bowel disease
- A family member who has had colon cancer
- A history of breast cancer
While colon cancer typically affects older adults, it can happen at any age. (Mayo Clinic. (2023, November 8). Colon cancer.)

Symptoms
Most early-stage colon cancers show no symptoms. However, the following symptoms may indicate colon cancer:
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Blood in stools (or black stools).
- Changes in bowel habits ( excessive diarrhea, constipation).
- Unexplained weight loss.
Diagnosis
With appropriate screening, colon cancer can be detected early:
- A rectal exam may reveal a mass in patients with advanced cancer, but not early-stage cancer.
- A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) detects small amounts of blood in the stool, which may suggest colon cancer.
Diagnosis
With appropriate screening, colon cancer can be detected early:
- A rectal exam may reveal a mass in patients with advanced cancer, but not early-stage cancer.
- A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) detects small amounts of blood in the stool, which may suggest colon cancer.
With appropriate screening, colon cancer can be detected early:
- Colonoscopy: a procedure that uses a long, flexible tube with a camera to examine the inside of the colon.
- Sigmoidoscopy: similar to a colonoscopy but used to examine only part of the colon.
As from 2024, Link to Life began providing the Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) to patients as part of its efforts to promote early detection of colorectal cancer. This non-invasive screening tool helps identify hidden blood in the stool, which can be an early sign of colon cancer, allowing for timely medical intervention and improved outcomes.
Preventive Measures
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Eat fresh fish 1–3 times per week.
- Increase fiber in your meals.
- Avoid high-fat foods.
- Reduce red meat intake.
- Stop smoking.
- Avoid alcoholic beverages.
Risk factors
You have a higher risk of colon cancer if you are:
- Age 60 and older
- Consume meals rich in red meat
- A cancer in other parts of your body
- Benign polyps
- An inflammatory bowel disease
- A family member who has had colon cancer
- A history of breast cancer
While colon cancer typically affects older adults, it can happen at any age. (Mayo Clinic. (2023, November 8). Colon cancer.)
The cancer: What You Need to Know
Cancer results from the abnormal and uncontrolled division of cells called cancerous cells, which invade and destroy surrounding tissues. Cancer usually begins with the formation of a lump or tumor. One of the biggest problems related to cancer is its ability to spread to other parts of the body, a process called metastasis.

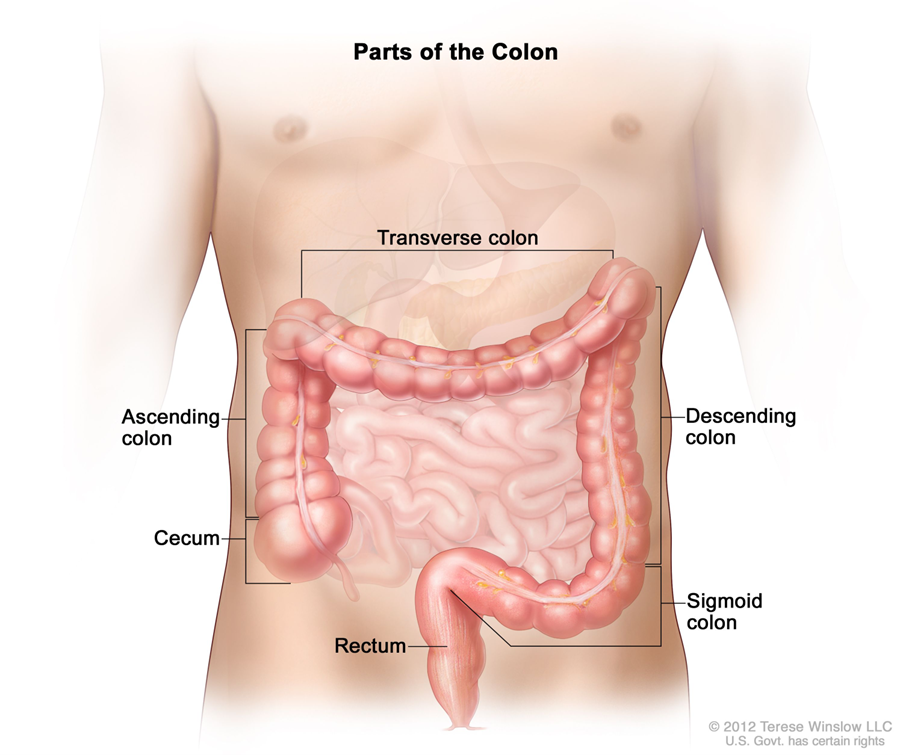
What is the colon?
The colon measures 1 to 1.5 meters in length and 4 to 8 centimeters in diameter. Also known as the “large intestine,” the colon forms the last part of the digestive system. It is made up of several parts:
- The cecum
- The ascending colon (right side)
- The transverse colon
- The descending colon (left side)
- The sigmoid colon
- The rectum
Functions of the colon:
- Transport waste to the rectum to eliminate it
- Absorb water from waste